Proteins are composed of sequences of subunits called amino acids.
We know 20 of them:
A = alanine C = cysteine D = aspartate E = glutamate F = phenylalanine
G = glycine H = histidine I = isoleucine K = lysine L = leucine
M = methionine N = asparagine P = proline Q = glutamine R = arginine
S = serine T = threonine V = valine W = tryptophan Y = tyrosine
The twenty amino acids can be assigned to a musical scale, for example the C-major scale below:
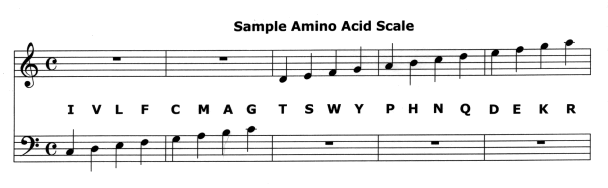
In this example the amino acids are ordered
from hydrophobic = water-insoluble (I «» c)
to hydrophilic = water-soluble (R «» a2), as far as possible.
The duration of each note varies with the number of DNA (DesoxyriboNucleic Acid) codons
associated with the amino acid.
The DNA codons are part of the genetic information for protein synthesis
on the chromosomes of each cell's nucleus.
The last three codons to sound are stop codons and do not correspond to any amino acid.
To make proteins function the right way,
allowing them to bind to or interact with other substances,
they are folded in three dimensions.
Here is the 3D-structure of Hemoglobin:
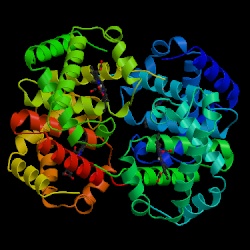
Different folds (or other features) may be assigned to different instruments.
For more detailed information please follow the link on the author page of Mary Anne Clark.
|
 - Wissenschaft & Kunst (Science & Art) -
- Wissenschaft & Kunst (Science & Art) -  - Wissenschaft & Kunst (Science & Art) -
- Wissenschaft & Kunst (Science & Art) -
 Details:
Details:
